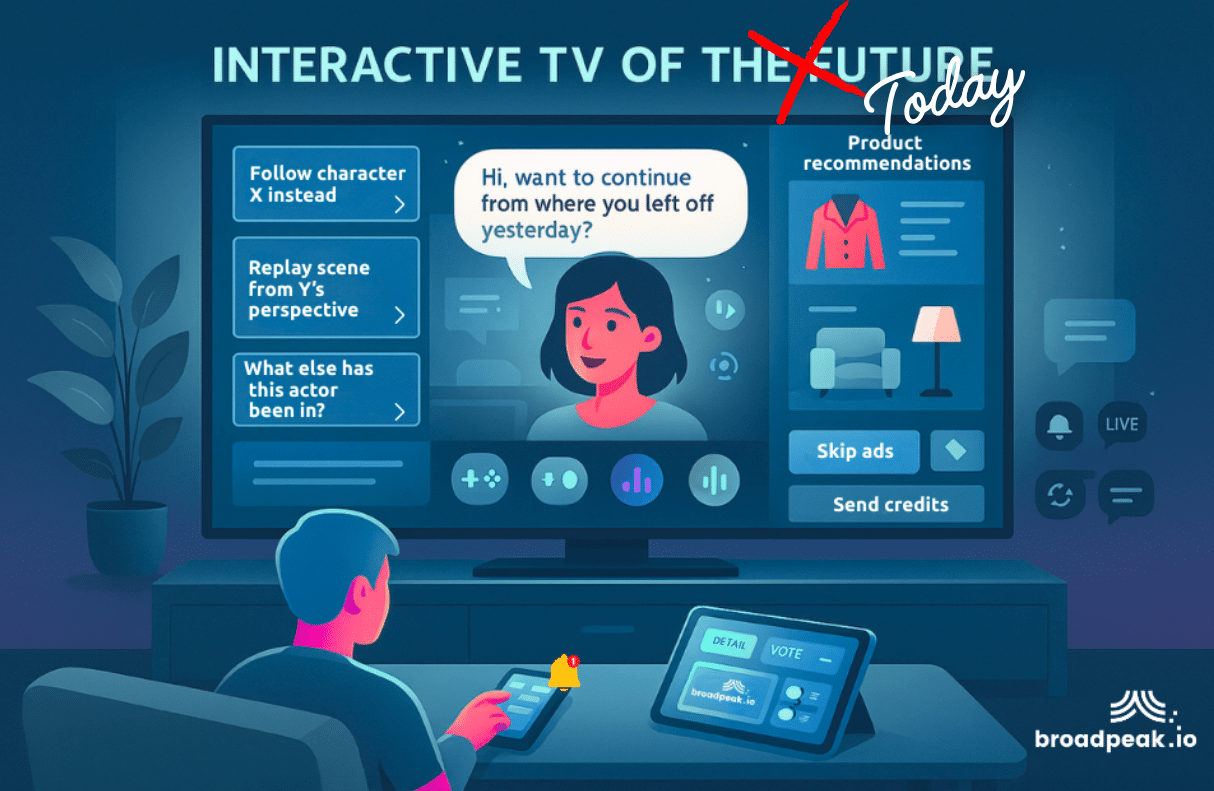
We live in an age where TV isn’t just something you watch; it adapts to you. With the rise of ad insertion and personalization, New TV, encompassing streaming services, social media, and other digital platforms, requires constant contextualization. For content providers, these evolutions mean increased engagement, viewer retention, and new monetization models.
So, how did we get here? How did interactive TV evolve from a novelty to an essential part of modern entertainment? Understanding the path to today’s interactive platforms highlights the strategic opportunities available across the OTT ecosystem. Let’s take a quick look at its development.
1. Early Experiments: The Interactive Promise
The idea of interactivity in TV wasn’t born yesterday. The concept of combining television with interactivity has existed since the beginning, but it wasn’t until the 1990s that real attempts began. Services like WebTV and the early digital cable boxes allowed viewers to browse the internet or access additional content while watching television. These early experiments were clunky, with limited functionality and slow internet speeds. But they planted the seed for what was to come. Real examples:
- Qube (USA, 1977-1984) – A cable TV service that allowed viewers to interact using a remote control for polls, quizzes, and alternative storylines.

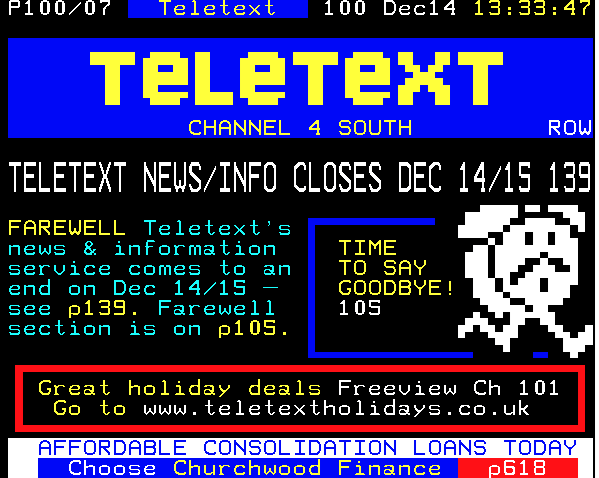
- Teletext (Europe, 1980s-2000s) – Early digital information service where viewers could access news, weather, and sports by inputting page numbers on their TV remote.
- “Interbang?” (Italy, 1984) – A quiz show where viewers could call in and answer questions.

- “Télé Match” (France, 1980s) – Featured interactive audience participation via phone-in voting.

- “Nightmare” (UK, 1987–1994) – An adventure game show where viewers controlled the actions of a player navigating a dungeon.
- “Você Decide” (Brazil, 1992-2000) – A pioneering interactive TV show where viewers called in to vote on how the episode would end.

“Hugo Délire” with Karen Cheryl (France, 1992) – A playful interactive TV show where the selected viewer had to avoid locomotives by pressing telephone keys to win a trip, depending on the final score.

2. The Rise of Digital TV and DVRs
By the 2000s, interactive TV began to see more tangible growth with the rise of Digital TV and DVRs. Interactive features like on-screen guides, pay-per-view, and VOD (Video On Demand) were introduced, giving viewers more control over what and when they watched. The real game-changer, however, was the DVR, which allowed viewers to pause, fast-forward, and skip ads altogether. This ability to control content considerably shifted how people consumed television, leading to a more personalized viewing experience.
Real examples:
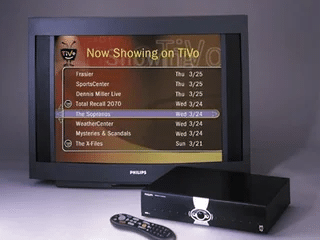
- TiVo (USA, 1999-present) – Introduced digital recording and skipping commercials, shifting viewer control.
- Sky Digital (UK, 1998-present) – Provided interactive features like betting, shopping, and alternative camera angles for sports events.
- “Big Brother” (global, 1999 –present) – Let viewers vote by phone or SMS to eliminate contestants in real time. The format was widely successful, with local editions in many countries and regions.
3. Streaming and the Personalization Revolution
With the advent of streaming services like Netflix, Hulu, and later, Disney+ and Amazon Prime, interactive TV reached a new level. Personalization became the norm, with algorithms suggesting content based on viewing history, preferences, and mood. But it wasn’t just about choosing what to watch. Streaming platforms began experimenting with interactivity on a whole new scale.
Netflix, for instance, launched Black Mirror: Bandersnatch, a choose-your-own-adventure film that let viewers make decisions for the protagonist, influencing the story’s outcome. It was an innovative use of interactivity, pushing the boundaries of passive viewing and allowing the audience to shape the narrative directly.
Real examples:
- “Black Mirror: Bandersnatch” (Netflix, 2018) is a choose-your-own-adventure film where viewers control the protagonist’s decisions.
- Amazon Prime X-Ray (2012-present) – Offers real-time actor information, trivia, and scene details while watching.
- HBO’s “Mosaic” (2017) – An interactive miniseries where viewers selected which character’s perspective to follow.
- Live Chat and Real-Time Interaction – Another major driver of interactivity is the live chat function during broadcasts. It’s not just about choosing your content – it’s about reacting and interacting in real time. For instance, during the Roland Garros final, the French broadcaster’s app featured a chat window alongside the live video stream. Viewers could comment, ask questions, or share reactions as the match unfolded. This kind of feature is standard on platforms like YouTube Live and Twitch, and it’s a core strength of apps like TikTok, where real-time comments, likes, and reactions are central to the viewing experience. Even when the chat isn’t used, its presence shapes how viewers expect to interact with live content. It turns viewing into a shared, social activity.
4. The Integration of Ads and Contextualization
Interactive TV is evolving with the integration of personalized advertising. Streaming services now employ data and AI to tailor ads based on user behavior, demographics, and real-time engagement. This personalization aims to make ads more relevant but also raises concerns about privacy and consumer autonomy.
Contextualization is central to this approach. New TV platforms must adapt to real-time user data to keep the experience engaging without being intrusive. For instance, YouTube has introduced “brand extensions,” allowing viewers to interact with ads on their connected TVs by sending product information directly to their phones, facilitating seamless shopping without interrupting the viewing experience.
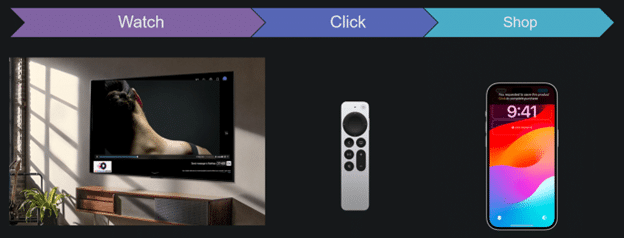
Similarly, broadpeak.io’s Click2® solution transforms traditional ads into interactive, shoppable experiences. Viewers can engage with ads using their remote controls and receive product details on their companion devices, enhancing engagement and providing measurable performance metrics for advertisers.
Key Technologies:
- broadpeak.io’s Click2® (2024-present): Enables interactive, shoppable ads across streaming devices, allowing viewers to engage via remote control and receive product information on companion devices.
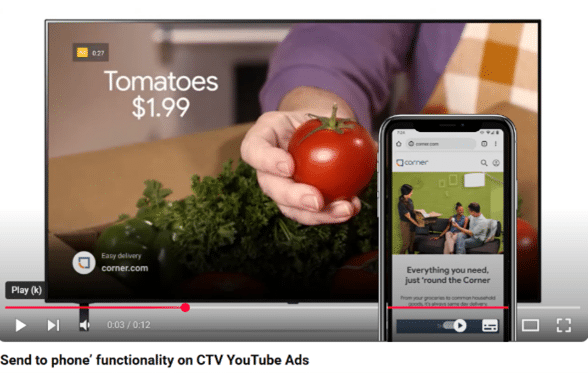
- YouTube’s Brand Extensions (2020-present): Introduces a “send to phone” feature in connected TV ads, directing viewers to product pages on their mobile devices without disrupting the viewing experience (source).
These advancements signify a shift towards more interactive and personalized advertising in streaming services, balancing user engagement with privacy considerations.
5. The Future of Interactive TV
The future of interactive TV lies in the deeper integration of emerging technologies like 5G, virtual reality (VR), and augmented reality (AR). 5G will enable faster, more seamless streaming, making immersive content more accessible. VR and AR will push engagement further, allowing viewers to step inside stories instead of just watching them.
Future AI tools may enable shows to adapt plotlines based on viewer preferences or feedback, ushering in a new era of hyper-personalized storytelling. The possibilities are endless. Interactive TV has evolved significantly, integrating various technologies to enhance viewer engagement. Here’s an overview of these advancements:
Human Interaction Options
- QR Code Scan: Viewers can scan on-screen QR codes with their smartphones to access additional content or participate in interactive features.
- Voice Control: Modern TVs incorporate voice assistants like Bixby, Alexa, and Google Assistant, enabling users to control their TVs, search for content, and adjust settings using voice commands.
- Remote Control: Traditional remotes have evolved to include voice activation and haptic feedback, offering more intuitive navigation and control.
Notification and Acknowledgement
- On-Screen Notifications: Interactive TVs can display real-time updates, such as sports scores or news alerts, keeping viewers informed without interrupting their viewing experience.
- Email and SMS Alerts: Users can receive personalized recommendations, updates, or promotional offers via email or text, enhancing engagement beyond the TV screen.
- Shopping Carts: Integration with merchandising platforms allows viewers to add products to a virtual cart directly from their TV, facilitating seamless shopping experiences.
Incentives
- Loyalty Programs (e.g., credits for ad-free content) – Viewers earn points or credits for engaging with content or advertisements, which can be redeemed for ad-free viewing or exclusive content.
- Commercial Incentives (e.g., discounts via interactive ads) – Interactive ads may offer coupons or discounts on products, encouraging viewer interaction and potential purchases.
- Free Gaming as Incentives: Complimentary games can be rewarded for engagement, adding an entertainment layer to the viewing experience.
Enabling the Link
- Companion Device Apps: Dedicated applications on smartphones or tablets synchronize with the TV, offering extended functionalities such as second-screen content or remote-control features.
- Device Pairing: Connecting a companion device to the TV enhances interactivity, allowing for personalized content delivery and control.
These advancements reflect a shift towards a more personalized and interactive viewing experience, catering to the evolving preferences of today’s audiences.
Conclusion – Your TV, Your Story
Interactive TV has transformed from a novelty into an essential part of modern entertainment. As streaming platforms become more tailored to individual preferences, the line between passive watching and active participation continues to blur. With hyper-personalized content and ad experiences becoming the norm, balancing engagement, convenience, and user privacy will be challenging.
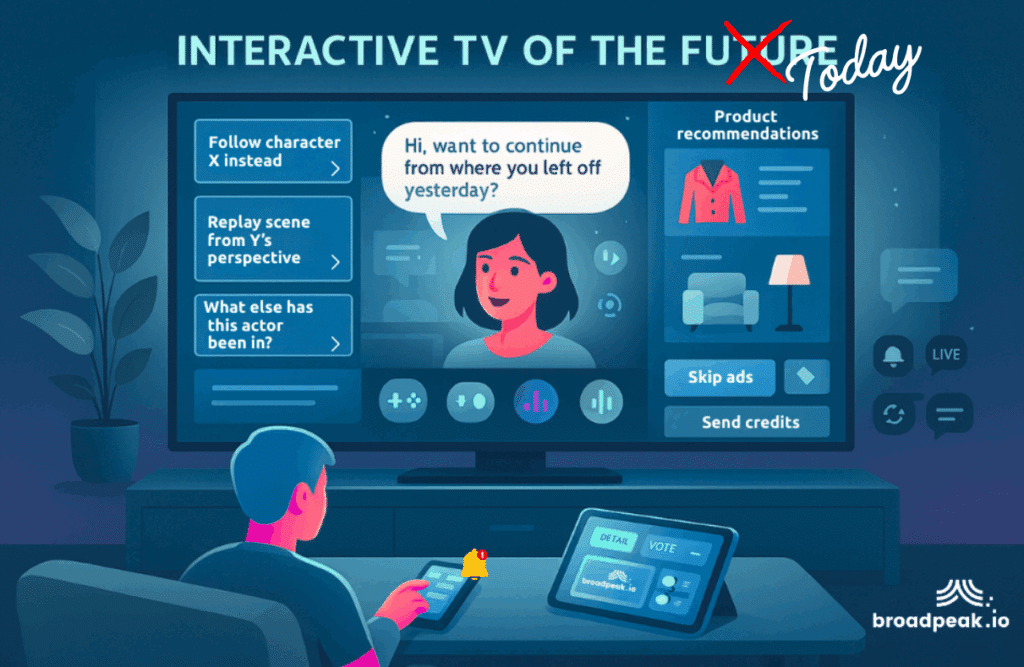
This shift is already underway. We are entering an era of ‘Ads You Actually Want’ and ‘Your TV, Your Story,’ where every screen delivers hyper-personalized content.
broadpeak.io is your partner in turning passive viewers into active participants.